Hypothermia in newborns occurs when body temperature falls below 36.5°C and is associated with increased risks of respiratory distress, infection, hypoglycemia, and death. Newborns lose heat rapidly due to their large body surface area, thin skin, and lack of insulating fat. Immediate and effective thermal management is therefore essential in neonatal care.
Newborn hypothermia can occur due to several mechanisms:
- Evaporation: Heat loss from wet skin immediately after birth
- Conduction: Contact with cold surfaces
- Convection: Exposure to cold air
- Radiation: Heat loss to cooler surrounding objects
These factors are particularly severe in preterm infants, making thermal protection a medical priority.
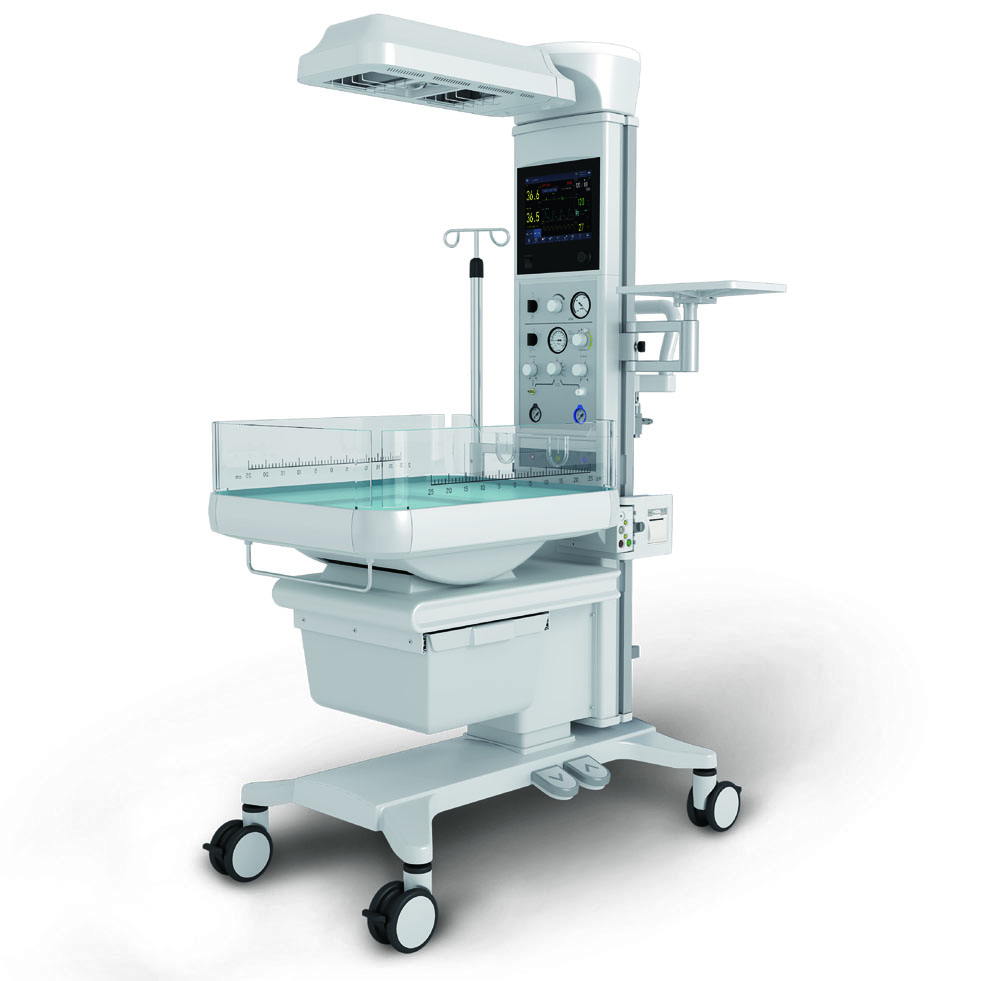
Infant warmers may play a crucial role in maintaining normothermia during postnatal care, resuscitation, and medical procedures. Unlike incubators, infant warmers provide open access to the infant while delivering consistent radiant heat, making them especially useful in delivery rooms and Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICU).
An infant warmer is a medical device that uses radiant heat to maintain the newborn’s body temperature within the normal range (36.5°C–37.5°C).
There are main components, include:
- Radiant Heating Element: Provides infrared heat to the infant
- Temperature Sensors: Measure skin and ambient temperature
- Control System: Automatically adjusts heat output
- User Interface: Displays temperature and system status
- Alarm System: Alerts caregivers to abnormal conditions
Infant warmer operates based on a closed-loop temperature control system. A temperature sensor placed on the infant’s skin continuously measures body temperature. The control unit compares this value with the preset target temperature. If the temperature drops below the setpoint, the heater increases output; if it rises above the limit, heating is reduced or stopped. This feedback mechanism ensures stable thermal regulation.
The Role of Infant Warmers in Preventing Hypothermia:
1 Immediate Post-Birth Care
Infant warmers provide rapid thermal stabilization immediately after delivery, especially during resuscitation procedures.
2 Care for Premature and Low Birth-Weight Infants
These infants have minimal fat stores and underdeveloped thermoregulation, making infant warmers essential for maintaining normothermia.
3 Support During Medical Procedures
Infant warmers allow healthcare providers full access to the newborn while preventing heat loss during examinations and interventions.
Use of infant warmers may offers several advantages in Clinical aspect, such:
- Reduced incidence of neonatal hypothermia
- Improved oxygen consumption and metabolic stability
- Lower risk of infection and complications
- Enhanced survival rates in high-risk newborns
- Improved workflow for healthcare professionals
As conclusion, Infant warmers are vital medical devices for preventing hypothermia in newborns, particularly in vulnerable populations such as premature and low-birth-weight infants. By providing a stable thermal environment, infant warmers significantly reduce complications and improve neonatal outcomes. Continued innovation and proper clinical use will further enhance their effectiveness in neonatal healthcare. (IW 2912)