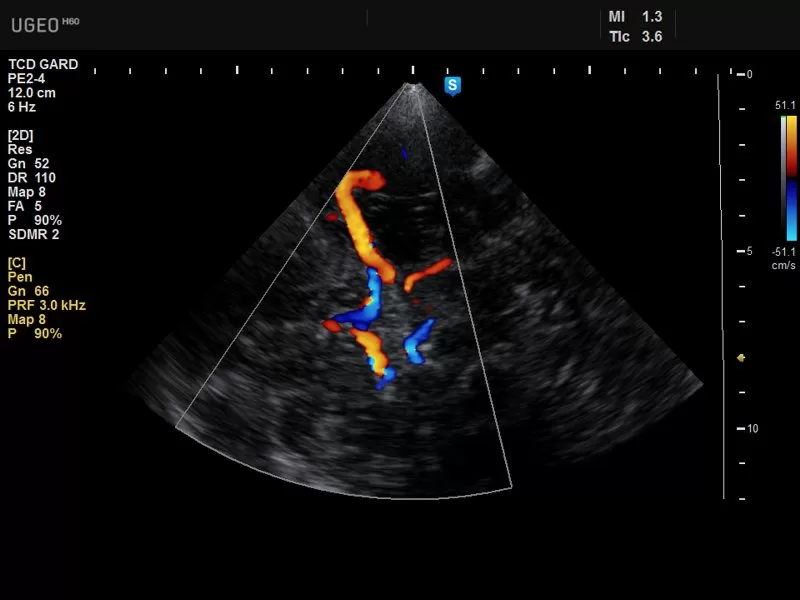
Ultrasound Doppler is a specialized imaging technique that utilizes sound waves to assess blood flow within the body. It combines the principles of conventional ultrasound imaging with Doppler effect technology, allowing for the visualization and analysis of blood flow patterns in real-time. The Doppler effect involves measuring changes in the frequency of sound waves reflected off moving objects, such as red blood cells, to determine the speed and direction of blood flow. In this article, we explore the applications and benefits of ultrasound Doppler in medical imaging.
Vascular Imaging:
Ultrasound Doppler is widely used in vascular imaging to evaluate blood flow in arteries, veins, and capillaries. It helps identify abnormalities such as blockages, narrowing of vessels (stenosis), and blood clots. By providing real-time visual feedback, ultrasound Doppler enables healthcare professionals to assess the severity and location of vascular conditions, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Obstetrics and Gynecology:
Ultrasound Doppler plays a crucial role in obstetrics and gynecology, particularly in monitoring fetal well-being and assessing the blood flow in the placenta and umbilical cord. Doppler ultrasound helps evaluate the resistance and pulsatility indices, which provide valuable information about fetal growth and development. Additionally, it assists in diagnosing conditions such as placental insufficiency and preeclampsia, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions regarding pregnancy management.
Cardiology:
In cardiology, ultrasound Doppler is used to evaluate blood flow within the heart and major blood vessels. It aids in diagnosing and assessing conditions such as valvular abnormalities, congenital heart defects, and heart failure. Doppler echocardiography enables the measurement of blood flow velocities, pressures, and gradients across the heart valves, providing valuable information about cardiac function and hemodynamics.
Peripheral Arterial Disease:
Ultrasound Doppler is a valuable tool for evaluating peripheral arterial disease (PAD), which involves the narrowing or blockage of arteries supplying the legs and arms. It helps assess the blood flow and detect any obstructions, providing vital information for the diagnosis and management of PAD. Doppler imaging can determine the ankle-brachial index (ABI), a non-invasive measure of peripheral arterial blood flow, aiding in the assessment of disease severity and guiding treatment decisions.
Non-Invasive Assessment:
One of the significant advantages of ultrasound Doppler is its non-invasive nature. It does not involve ionizing radiation or require contrast agents, making it a safe imaging modality for patients of all ages, including pregnant women. The real-time nature of Doppler imaging allows for immediate visualization and interpretation of blood flow patterns, facilitating quick diagnosis and timely intervention.
Conclusion:
Ultrasound Doppler is a valuable imaging technique that provides crucial information about blood flow patterns in various medical applications. From vascular imaging to obstetrics, cardiology, and peripheral arterial disease assessment, it offers non-invasive and real-time visualization of blood flow, aiding in the diagnosis, management, and treatment planning of various conditions. As technology continues to advance, ultrasound Doppler will likely continue to play a vital role in enhancing medical imaging and improving patient care