Patient safety is a core principle of healthcare delivery. As medical treatments become more complex, reliance on infusion technologies such as syringe pumps continues to grow.
Syringe pumps are widely used medical devices designed to deliver precise volumes of fluids and medications at controlled rates. They are essential in critical care, anesthesia, neonatal care, and oncology, where accuracy and consistency of drug delivery directly affect patient outcomes. Syringe pumps allow clinicians to administer potent drugs—such as vasoactive agents, insulin, opioids, and chemotherapy—with high precision. However, small errors in setup or programming can result in significant underdosing or overdosing, potentially causing serious harm.
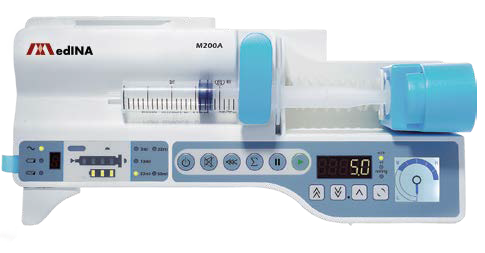
A syringe pump is a motor-driven device that holds a syringe and advances the plunger at a controlled rate to deliver fluids intravenously or via other routes. Unlike volumetric infusion pumps, syringe pumps are particularly suited for low-volume, high-accuracy infusions.
There are some key components:
- Syringe holder and plunger driver: Secure and advance the syringe
- Control panel/interface: Allows programming of rate, volume, and time
- Alarm system: Alerts users to occlusion, empty syringe, low battery, or malfunction
- Power supply: Mains electricity with battery backup
The Syringe pumps are commonly used in:
- Emergency departments
- Intensive care units (ICUs)
- Neonatal and pediatric care
- Anesthesia and pain management
- Oncology and palliative care
Their ability to deliver very small, accurate doses makes them indispensable for vulnerable patient populations such as neonates and critically ill patients.
Healthcare institutions play a key role in syringe pump safety by establishing policies, supporting reporting of near-misses, and fostering a culture of safety. Incident analysis and feedback loops help prevent recurrence of errors and promote continuous improvement.
In conclusion, Syringe pumps are one of vital tools in modern healthcare, offering precise and reliable drug delivery when used correctly. However, they also introduce potential risks that can compromise patient safety. Through proper training, standardized practices, smart technology, and organizational support, these risks can be minimized. A proactive approach to syringe pump safety ultimately improves patient outcomes and strengthens the overall quality of care. (IW 2601)
Ref:
- Institute for Safe Medication Practices (ISMP): Guidelines for Safe Infusion Pump Use
- ECRI Institute: Infusion Pump Safety Resources